/ Saving Lives through Innovative Technology
Designed to prevent accidents and save lives, ADAS is a collection of several systems with features that can help guide driver decisions in real-time as conditions change and enable human-free operations.
Radar, LIDAR, cameras, and ultrasound sensors are strategically placed throughout the exterior to give a 360-degree view and execute safety functions as necessary. In-cabin cameras are also used to monitor driver alertness and react accordingly, while passenger occupancy monitors adapt seatbelt and airbag settings if a child is detected in the front seat.
Depending on the make and design of the vehicle, ADAS functions may include some or all of the following:
Safety and collision avoidance:
- Adaptive cruise control (ACC)
- Automatic emergency braking (AEB) with pedestrian detection
- Blind spot detection (BSD)
- Collision avoidance system (CAS)
- Cross-traffic alert (CTA)
- Driver monitoring system (DMS)
- Drowsy driver detection (DDD)
- Emergency driver assist (EDA)
- Forward collision warning (FCW)
- Highway assist (HA)
- Lane change assist
- Lane departure warning (LDW)
- Lane keeping assistance (LKA)
- Night vision system (NVS)
- Surround view system (SVS)
- Tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS)
- Traffic sign recognition (TSR)
- Turning assistant (TA)
- Vehicular communication systems (V2X)
- Wrong way driving warning (WWDW)
Parking and maneuver assistance:
- Automatic parking system (APS)
- Parallel parking assist
- Park distance control (PDC)
- Perpendicular parking assist
Comfort and convenience:
- Adaptive headlights
- Adaptive high beam control (AHBC)
- Head-up display (HUD)
- Rain-sensing wipers
- Traffic jam assist (TJA)
Fuel efficiency and emissions reduction:
- Eco-driving mode
- Intelligent speed adaptation (ISA)
- Predictive cruise control
/ Application Considerations
Best-in-class components are required for the optimal performance of ADAS sensor modules. Engineers should consider the following:
- ESD protection - sensing technologies and other components must be protected from damaging electrostatic discharge
- Component size - several systems make up ADAS and there’s limited space in the vehicle to house all of the necessary components, so the smaller the better
- Reliability in harsh conditions - fluctuating temperatures, vibration, and shocks are a few of the environments design engineers should account for to prevent system failure
- Reverse battery protection - designs must incorporate safeguards to prevent reverse polarity in the battery
- Thermal performance - maintaining proper heat dissipation and minimal energy losses while executing multiple functions is essential for effective ADAS sensor module design
- Efficiency - ADAS sensor modules should operate as efficiently as possible without sacrificing reliability
- Cost - these advanced components must be robust enough to perform but also affordable enough to be used in vehicles to keep costs reasonable for consumers
- Applicable industry standards - ADAS components must meet stringent auto standards, such as AEC-Q101 qualification
/ ADAS: Prevent Accidents & Enhance Safety
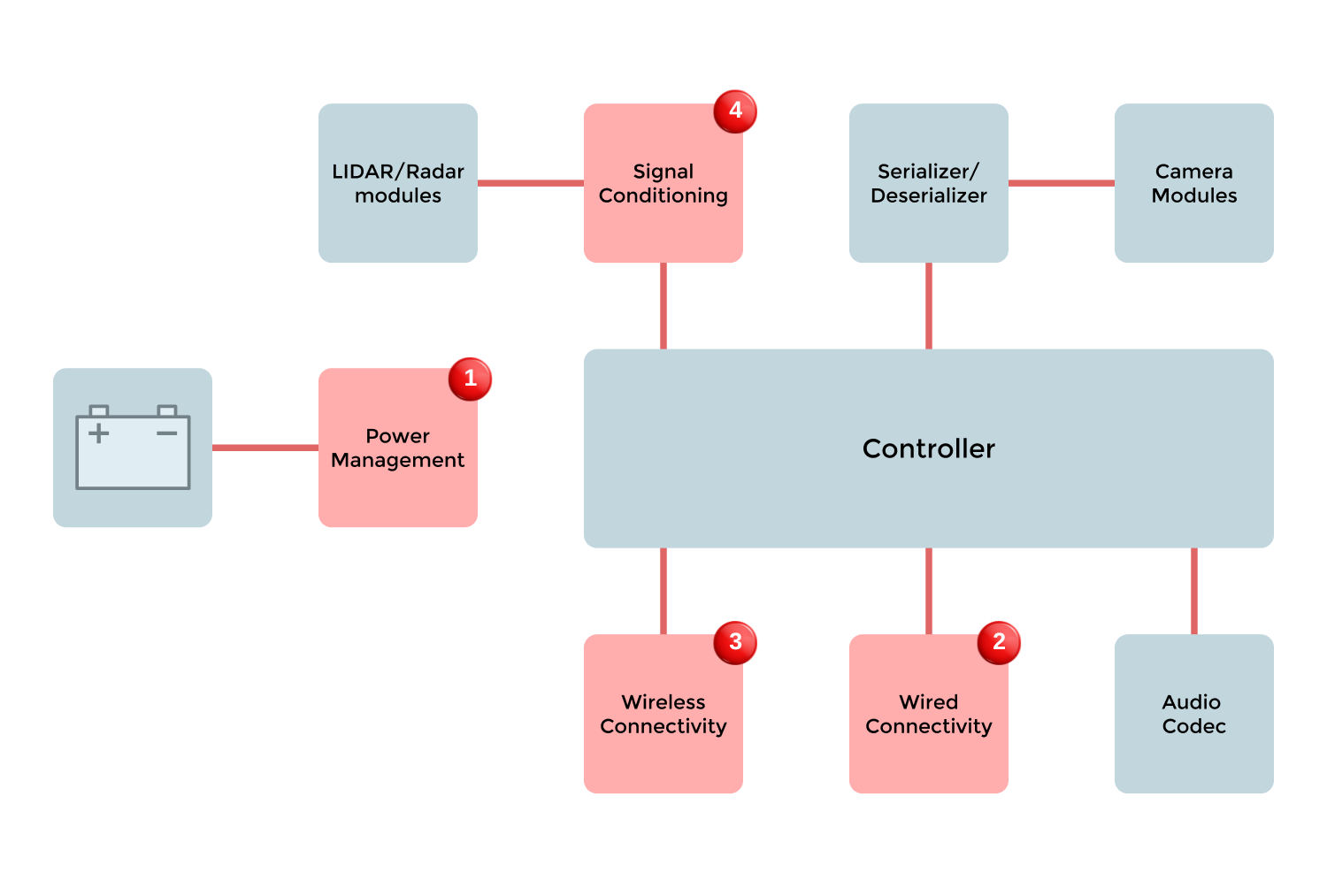
/ Block Diagram
/Recommended Products
Get a Competitive Edge on Your Next Project
No matter the application or industry, MCC has the components and service you need to get to market faster and reduce overall costs.
EXPLORE AUTO APPLICATIONS